Chronic pain after whiplash?
Whiplash, in addition to immediate structural damage, may hide an insidious long-term consequence: the misalignment of the Atlas vertebra and, in some cases, the Axis or other underlying vertebrae. This trauma may also worsen a pre-existing cervical misalignment, increasing the risk of future problems.
The "whiplash" occurs when the cervical spine undergoes a violent and sudden movement, first backward and then forward. It can happen during a car accident, a seemingly harmless fall, or during work or sports activities.
According to the U.S. occupational safety and health agency, 47% of children suffer a fall with a head impact within their first year of life. Between the ages of 2 and 5, children have already experienced around 200 falls, while by age 10, they have accumulated over 1,500 traumas of various kinds.
Despite the saying "What doesn't kill you makes you stronger," some seemingly minor falls can leave lasting effects that will endure for a lifetime.
Why do some people not recover after whiplash?
As you continue reading, you will discover why, after whiplash, some people are never the same and how even normal daily activities become a burden. In the most severe cases, it may become impossible to continue working properly, leading to emotional isolation with serious repercussions on social life.
What is usually diagnosed after whiplash are structural damage or the stretching of certain ligaments and muscles in the cervical spine. In the most serious cases, vertebral fractures or tears in ligaments and soft tissues are observed. However, beyond these obvious signs, the true reasons why some individuals develop chronic pain after whiplash, without apparent structural causes, remain largely unknown to medicine.
Whiplash: many questions

- Have you experienced whiplash and no doctor has been able to identify the cause of the chronic symptoms that continue to torment you over time?
- Have you exhausted all available diagnostic and therapeutic options without making any progress?
- Has your doctor performed X-rays, MRIs, or other tests, assuring you that structurally everything is normal?
- Despite the doctor's assurances, do your symptoms continue to worsen, leaving you dependent on painkillers or even psychotropic drugs (antidepressants)?
Your doctor may have tried to convince you that your symptoms are purely psychosomatic or even labeled you as a "hypochondriac," someone who "is just making a scene." However, you know perfectly well that your pain is real and that before the whiplash, you had nothing of the sort.
The problem is this: after whiplash, medical practice rightly focuses on looking for serious structural damage, such as bone fractures or ligament injuries. If such damage is not found, the doctor concludes that there is nothing significant, simply recommending rest, perhaps with the use of an immobilizing cervical collar.
However, a whiplash trauma does not always cause obvious and easily diagnosable injuries. Even seemingly mild imbalances and misalignments of the cervical vertebrae, if neglected or underestimated, can gradually develop into chronic disorders over time.
The cervical spine: a precision mechanism

The cervical spine can be compared to a precision mechanism.
Here's an example to help you understand better: imagine dropping a mechanical watch on the floor. You pick it up, and at first glance, it seems intact, but over time you notice that the watch is consistently running late. In the complex internal mechanism, it's likely that one of the pivots on which the gears rotate has become deformed, increasing friction between the delicate components and compromising its proper functioning.
Something similar can happen to the cervical spine: although whiplash may not cause deformities in the vertebrae, they can lose their proper alignment, both with each other and with the skull, disrupting the balance of the entire spinal column.
Typically, vertebral misalignments are not considered by conventional medicine. One reason is that slight shifts in vertebrae are not sufficiently evident on X-rays or MRIs. Doctors focus on searching for obvious structural damage, often overlooking functional misalignments of the vertebrae.
Another issue that completely eludes standard diagnostic tests is the abnormal compression of nerves and blood vessels that cervical vertebrae can cause when they deviate from their ideal alignment following a whiplash. More specific tests, such as angiography, might reveal a reduction in blood flow, but these are invasive procedures that are generally avoided. What makes the diagnosis even more difficult is that, for a reliable comparison, measurements would need to be taken both before and after the traumatic event. However, in the case of whiplash, unless you had already undergone the same test in the past for other reasons, only post-injury measurements are possible. The same applies to a Doppler ultrasound: without a previous reference value, any comparison is meaningless because it cannot be ruled out that the detected condition is congenital and thus unrelated to the accident.
As a result, the doctor arrives at the verdict "the persistence of symptoms after whiplash is of unknown cause" and, even worse, asserts that a full recovery is unlikely and should be ruled out.
Returning to the watch example: what would you think if the watchmaker, instead of repairing the defective mechanism, told you that it’s not the watch showing the wrong time, but YOU who can no longer read it correctly? Wouldn't you think the watchmaker was out of his mind? Yet, a similar reasoning is accepted without objection when made by a doctor, considered normal, even though it concerns your health—the most precious asset you have. People end up resigning themselves to the idea that "it is what it is, and nothing can be done" for most chronic disorders. How many times have you heard phrases like: "you can’t recover from your condition", "you have to learn to live with it", "it’s a psychosomatic condition" or "your condition is imaginary"?
With AtlantoMed, we finally have a method to restore the balance of the cervical spine after whiplash.
It’s important to emphasize that AtlantoMed does not treat structural damage such as broken bones or injured muscles and ligaments, which must always be diagnosed and treated by a doctor. Additionally, we do not perform cervical manipulations or limit ourselves to a simple massage: our approach is unique and aimed at restoring proper vertebral balance.
An interesting fact: it has occasionally happened that a whiplash had the opposite effect, favoring the realignment of vertebrae and leading to the disappearance of pre-existing symptoms. However, these are rare and random occurrences, so we do not recommend it as a therapeutic method ;).
What exactly happens during whiplash?
Whiplash victims, who after undergoing all conventional examinations and treatments fail to fully recover, often feel that something in their neck is not the same as before. In most cases, this perception reflects reality.
This condition can lead to an alteration in cerebrospinal fluid flow, the compression of important blood vessels in the neck, and lymphatic channels—consequences that are nearly impossible to diagnose using standard instrumental tests.
Once the misalignment of the Atlas is established, if not corrected with an effective technique like AtlantoMed, the typical chronic symptoms of whiplash may develop over time.
Delayed symptoms after whiplash
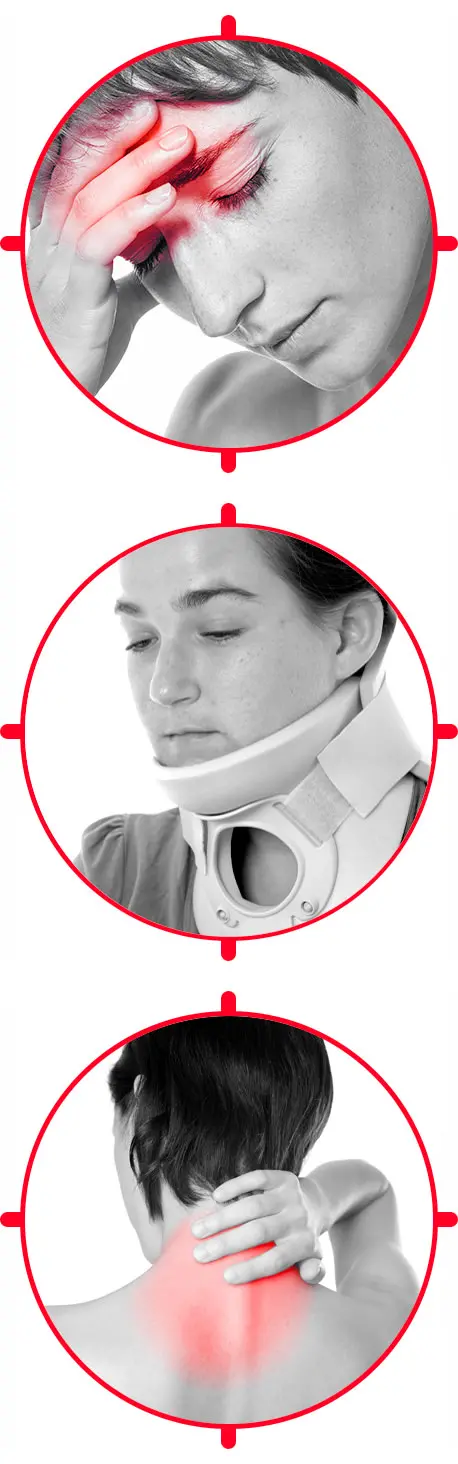
- neck and shoulder muscle pain
- sensation of a heavy head
- oppressive headaches – tension headaches – migraines
- tingling in the face or arms
- fatigue – mental fog
- vision disturbances
- hearing disturbances – tinnitus – ringing in the ears
- problems with concentration and memory
- sleep disorders – chronic fatigue syndrome
- insecurity and anxiety
- irritability – increased sensitivity to noise
- weakness – reduced physical and mental performance
- dizziness – vertigo – sense of instability
- depression – distress – discouragement
- burnout syndrome
Chronic contraction of cervical muscles after whiplash
Many people who have suffered a whiplash experience the same unpleasant situation: the pain caused by the trauma, instead of subsiding, progressively worsens, becoming chronic and turning into a nightmare.
The cause lies not only in the pronounced misalignment of the Atlas but also in the excessive tension of the deep cervical musculature, which develops as a result of the trauma and is maintained by the body for protective purposes.
The neck muscles, overstressed during the trauma, remain permanently tense and shorten. This chronic tension is not alleviated even by repeated massages or physiotherapy treatments, as the muscles involved are located deep and are not easily reachable manually. Consequently, head movements are often restricted and accompanied by persistent pain.
Straightening of the Cervical Lordosis
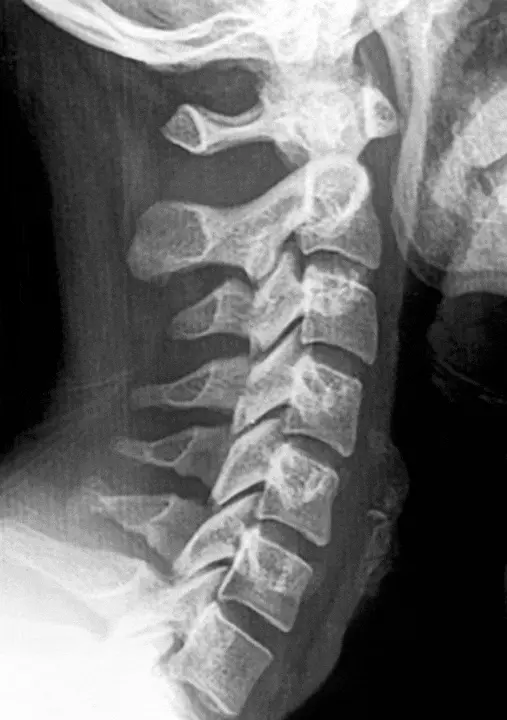
Straightening of the cervical lordosis, loss of cervical lordosis, and loss of physiological curvature are terms that describe the same condition, in which the cervical spine becomes abnormally straight, altering its natural curve.
After whiplash, the loss of physiological cervical lordosis is very common and often underestimated. Long-term consequences appear insidiously, with a negative impact on health.
If the straightening of the cervical lordosis persists without adequate correction, symptoms, whether mild or severe, tend to worsen, with the risk of developing irreversible degeneration of the cervical spine.
When consulting a doctor after an accident, attention is often focused on structural damage, such as fractures or other visible injuries. While these checks are essential for identifying serious issues, who addresses the functional problem? Is a physiotherapist consulted? Unfortunately, even then, the treatment is often symptomatic without effectively restoring the physiological cervical curvature.
To address this issue, we have developed a specific program to restore the natural curvature: straightening of the cervical lordosis.
What to do after whiplash
The AtlantoVib devices with vibro-resonance are specifically designed to correct the Atlas and reach deep musculature through an intense and highly effective massage.
With one or two sessions focused primarily on the cervical area, the contracted muscles can relax again. Once the contractures are resolved, the head will regain its freedom of movement, providing significant relief.
This type of vibro-resonance massage, combined with the correction of the Atlas misalignment, has successfully led to the remission of whiplash disorders, even in cases considered "unsolvable."
Precautions After Whiplash

Since the AtlantoMed treatment stresses the atlanto-occipital ligaments and related structures, certain precautions are necessary before proceeding after whiplash. It is important to conduct a thorough medical examination with appropriate dynamic radiological investigations before Atlas correction, to rule out any structural damage to the cervical spine caused by the trauma. See also: Cervical Instability.
Depending on the severity of the whiplash injury, it is advisable to wait one to two months before undergoing AtlantoMed treatment, to allow for the healing of any undetected structural damage.
Following Atlas correction, additional manual therapies may be recommended to promote the rebalancing of the rest of the spine.
High School Thesis: Whiplash - Treatment with AtlantoMed
Whiplash Video Interview
Testimonials After Atlas Realignment
Some Testimonials from the Forum
- Question: Whiplash: 35 Years of Cervical Pain Resolved
- Marta: Horseback Riding Fall with Whiplash
- Gessica: Migraine Post-Accident with Whiplash
- Lusy: Whiplash: 6 Years of Suffering and I Am Reborn
- Laura: Headaches Resolved After Cervical Trauma
- Ilaria: Whiplash with Migraine
- More Testimonials: Whiplash
What People Say About Us
Beware of those who disguise a simple cervical manipulation as Atlas realignment and those who offer low-quality imitations of our method. The results speak for themselves: over 10,000 testimonials and reviews in various languages make us unique. Click to discover opinions, ratings, and authentic experiences shared by those who have experienced Atlas correction with Vibro-Resonance AtlantoMed:
Scientific Literature on Whiplash

- Relationship Between Misalignment, Obstruction of Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow.
- Linking Hypermobility Pain Disorders with Their Multi-Systemic Comorbidities.
- Atlantoaxial Rotary Subluxation After Minor Trauma.
- Atlantoaxial Rotary Subluxation in Children.
- Chronic C1-C2 Rotatory Subluxation Reduced by C1 Lateral Mass Screws and C2.
- Connection Between the Spinal Dura Mater and Suboccipital Musculature.
- Occipitocervical Dislocation in Low-Energy Trauma.
- Cervical Lordosis: Increased Cerebral Blood Flow.



