ATLAS CORRECTION: Why Is It So Important?
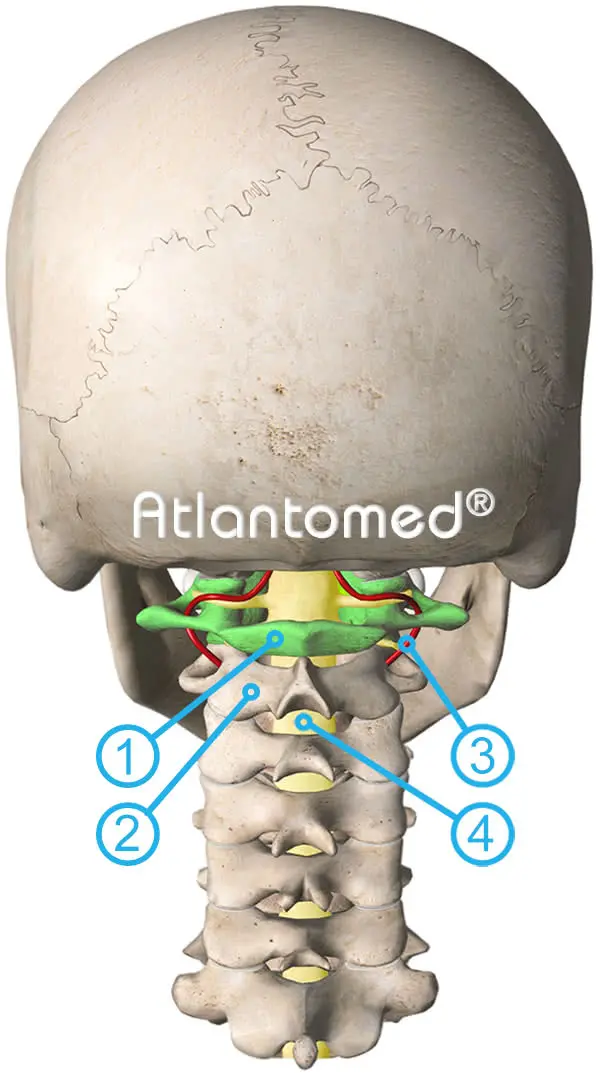
2) Axis
3) Vertebral Artery
4) Spinal Cord
The mythological figure of the Titan Atlas, condemned to bear the weight of the celestial vault on his shoulders for eternity, inspired the name of the first cervical vertebra, also called the Atlas. This vertebra, located at the base of the skull, indeed supports the weight of the head.
The Atlas vertebra plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural and functional balance of the body. Acting as a connecting point between the head and the spine, it allows for smooth movements of head tilting and flexing, while its interaction with the second vertebra, the Axis, enables head rotation.

Even a slight misalignment of the Atlas from its anatomically and physiologically neutral position can trigger a domino effect with negative repercussions on the entire body's functioning: the body tends to "collapse", reducing height, disrupting communication between the brain and the rest of the body with potential neurological consequences, and impairing blood circulation to the skull.
Difference Between Static and Dynamic Load
To better understand the issue, it is essential to distinguish between the static and dynamic conditions. When the body is in motion, the distribution of weight and forces dynamically impact the musculoskeletal system. Muscles under stress can cause temporary compression of nerves and blood vessels, but these temporary compressions are tolerated without consequences because they are dynamically variable. After exertion, when the body returns to a state of rest, the compressions cease.
In contrast, the static load constantly weighs on the skeleton under the force of gravity. If this load is permanently unbalanced and unilateral, it results in compromised posture and persistent compression of nerves and blood vessels, potentially leading to various dysfunctions.
What Does a Misaligned Atlas Have in Common with the Leaning Tower of Pisa?
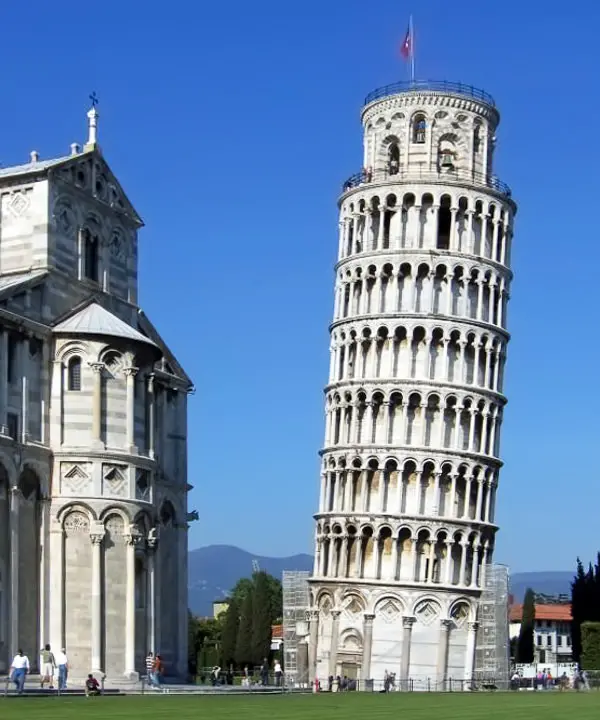

A fitting example to understand what happens to the human body's statics when the Atlas vertebra is misaligned is the Leaning Tower of Pisa in Italy: the upper part was added when the tower was already leaning. While this may be considered an acceptable compromise in architecture, it is absolutely not for the human body’s balance.
The automatic reflex that tends to keep the head level affects the entire body's statics, altering posture and triggering a series of side effects resulting from this imbalance.
This is why correcting the Atlas is essential for preserving health and preventing pain. Before AtlantoMed, it was difficult, if not impossible, to provide a long-lasting resolution for chronic dysfunction of the upper cervical spine.
The Small Bone with Big Effects
The Atlas, though a small vertebra that might seem insignificant, plays a crucial role comparable to the keystone of an arch: without it, the entire structure would collapse.
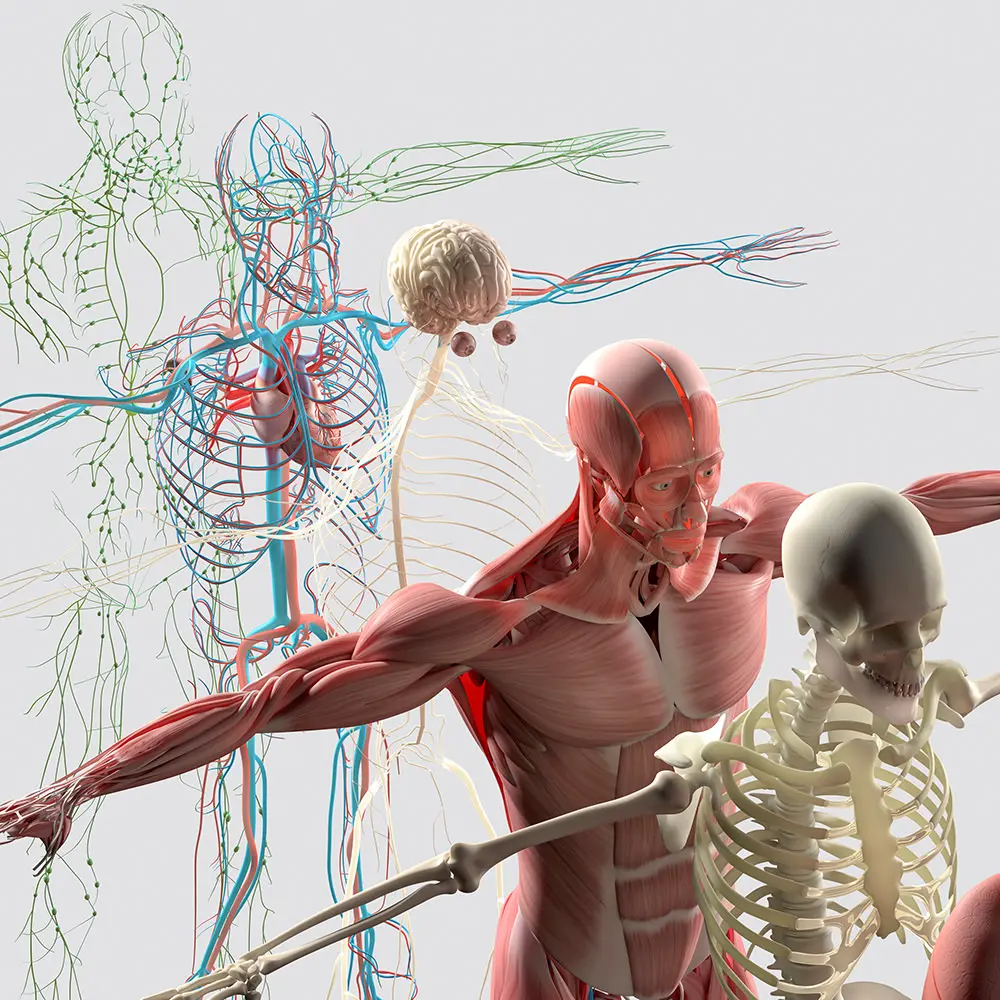
The negative effects of a misalignment of the first cervical vertebra are not limited to the specific area but propagate throughout the body, compromising overall balance. These repercussions involve the skeletal system, the muscular system, the nervous system, the cardiovascular system, and finally, the lymphatic system.
Proper alignment of this vertebra is therefore essential to maintaining correct posture and ensuring the harmonious functioning of the entire body.
The Consequences of a Misaligned Atlas
When the skull rests on a misaligned Atlas, the balance organ, together with cervical proprioceptors and the eyes, still tries to align itself with the horizon. The result is constantly tense ligaments and muscles in the sub-occipital area, straining to compensate for the head’s defective alignment and causing a compensatory adaptation of the entire spine, which then curves accordingly.
This continuous effort, over time, can lead to pain and muscle stiffness, especially in undertrained muscles. The resulting problems include neck pain, tension headaches, dizziness, torticollis, and pain or limited movement in turning the head. While strengthening cervical muscles may provide some relief, the optimal solution is to eliminate the cause of the imbalance.
Effects on the Axis and Other Cervical Vertebrae
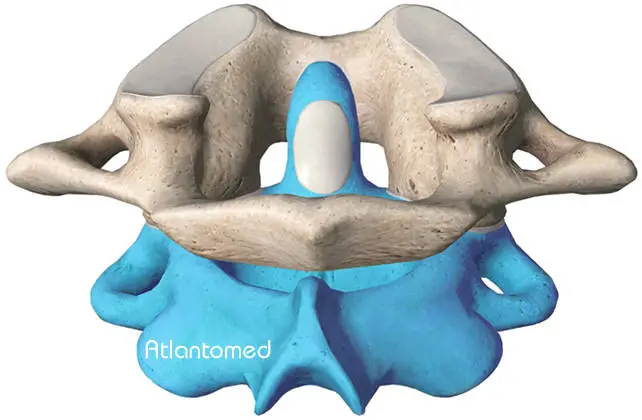
Depending on the type of Atlas misalignment, negative effects can also be observed on the alignment of the Axis (second cervical vertebra or C2).
During Atlas alignment, if necessary, the Axis is also realigned. The other underlying vertebrae then adjust accordingly. After AtlantoMed treatment, it is generally no longer necessary or advisable to undergo further chiropractic or osteopathic treatments for blocked vertebrae.
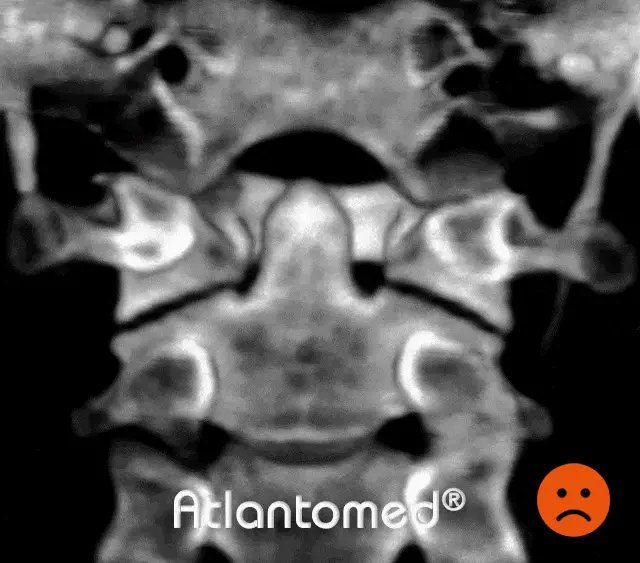
BEFORE
AFTER ATLANTOMED
This 3D reconstruction of a spiral CT shows a section of the upper cervical vertebrae viewed from behind, before and after Atlas correction using AtlantoMed vibro-resonance.
After the treatment, there is a clear improvement in the alignment of the first Atlas vertebra relative to the occipital bone and the second vertebra.
The Axis's dens appears more centered in its articulation with the Atlas, while the skull is better balanced, without the previous tilt to the right.
These images clearly demonstrate the success of the treatment in restoring proper alignment of the cervical structures.
Atlas Alignment Influences the Entire Body
Atlas misalignment can trigger a chain reaction, causing general skeletal asymmetry, such as: one shoulder higher than the other with scapular pain, scoliosis, tilted pelvis with a risk of herniated discs (discopathies), back pain, hip pain, knee pain, and even foot issues.
An altered posture promotes the development of chronic muscle stiffness, which causes pain and blockages (subluxations) of other vertebrae. This results in compression of the nerve roots exiting the spine, which over time become irritated. To treat the irritation, doctors increasingly resort to corticosteroids, very useful drugs that, however, over time produce significant side effects.
Compression of specific nerve endings can cause tingling, a sensation of "numb" limbs, or malfunction of the corresponding innervated organs, leading to a series of disorders, even in seemingly unrelated areas of the body.
Hardened and thickened muscles due to constant strain also compress lymphatic channels and blood vessels passing through them, reducing vascularization and causing waste buildup in the tissues. This condition creates a vicious cycle that makes muscles increasingly rigid.
While other factors, such as cranio-mandibular dysfunctions and scars, can influence posture, the Atlas position is crucial. Thousands of postural photos taken systematically before and after treatment show how the skeleton can regain a more natural and correct shape without further interventions beyond Atlas correction.
If you constantly have one shoulder higher than the other or a tilted pelvis, discomfort and pain are inevitable sooner or later!
What Are the Effects of Atlas Misalignment on Posture?
When the vertebrae of the spine are in balance, weight is evenly distributed on both sides of the skeleton.
The head rests on the Atlas, weighing a significant 5-6 kg. A misaligned Atlas distributes this weight unevenly on the spine.
This condition alters the body's center of gravity, causing imbalance that extends to the feet. It results in joint blockages along the spine, accompanied by musculoskeletal dysfunctions.
One side of the body is more stressed than the other. This is why pain usually concentrates on one side.
The imbalance can be measured using two ordinary scales, which may show a weight difference of up to 20 kg between one leg and the other. Depending on the type of misalignment, the physiological kyphosis or lordosis of the spine may either increase or disappear. See also: Scoliotic posture.
Visible Effects of Atlas Correction on Posture
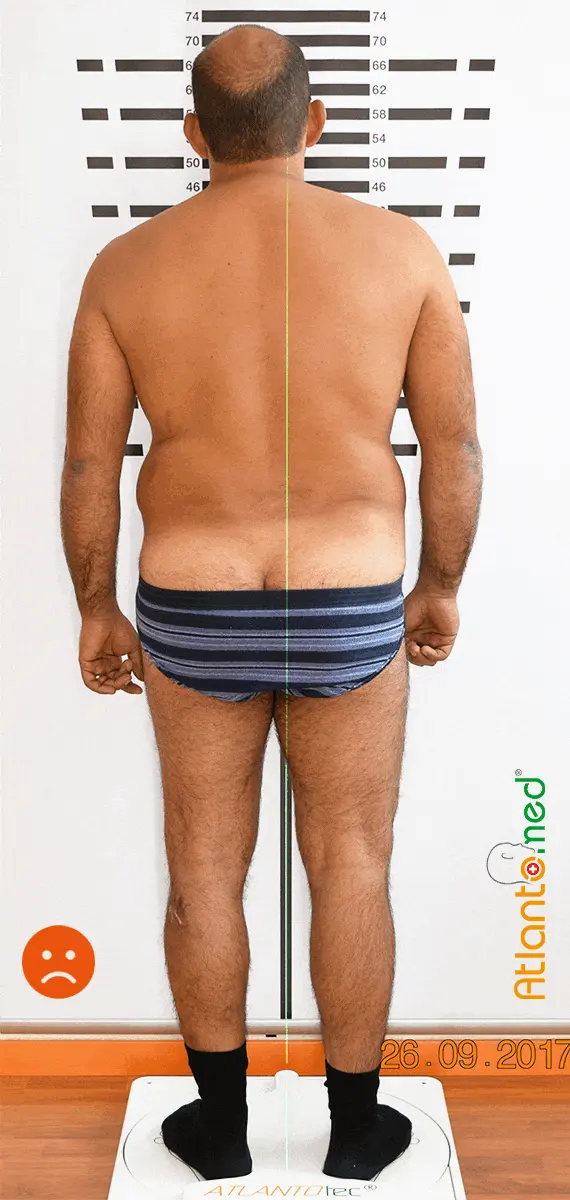
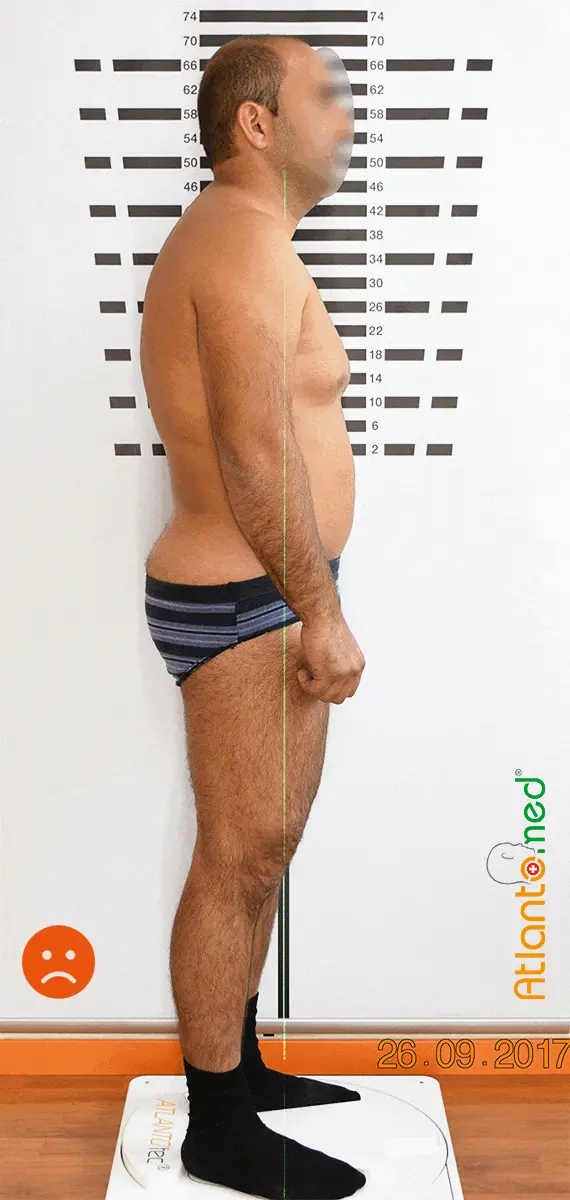
BEFORE
AFTER ATLANTOMED
Are Your Issues Really Just Psychosomatic?

How many patients have heard their doctor say that the cause of their symptoms is unknown or attributed to a psychosomatic origin? This is a diagnosis that leaves patients dissatisfied, as it offers no concrete explanations or real solutions. Symptoms often represent just the tip of the iceberg of a deeper problem that the doctor may not be able to identify, attributing them instead to the psyche. A common example is the disorders that can occur after whiplash: migraines, recurrent headaches, cervical stiffness, and other chronic issues.
After the AtlantoMed treatment, significant improvements are often observed, not only in perceived symptoms but also in overall posture. Issues such as functional short leg, hyperlordosis, kyphosis, and loss of physiological cervical lordosis are often reduced or eliminated. So before accepting that your issues are "just psychosomatic," consider whether Atlas misalignment might be the true problem to address. The treatment not only helps eliminate the continuous use of symptomatic drugs but also often avoids the need for psychotropic medications.
What People Say About Us
Beware of those who disguise a simple cervical manipulation as Atlas realignment and those who offer low-quality imitations of our method. The results speak for themselves: over 10,000 testimonials and reviews in various languages make us unique. Click to discover opinions, ratings, and authentic experiences shared by those who have experienced Atlas correction with Vibro-Resonance AtlantoMed:



